How Local AI Can Automate Marketing & Digital Media Tasks
💡 Important: Consumer-Grade Hardware Focus
This guide focuses on consumer-grade GPUs and AI setups suitable for individuals and small teams. However, larger organizations with substantial budgets can deploy multi-GPU, TPU, or NPU clusters to run significantly more powerful local AI models that approach or match Claude AI-level intelligence. With enterprise-grade hardware infrastructure, local AI can deliver state-of-the-art performance while maintaining complete data privacy and control.
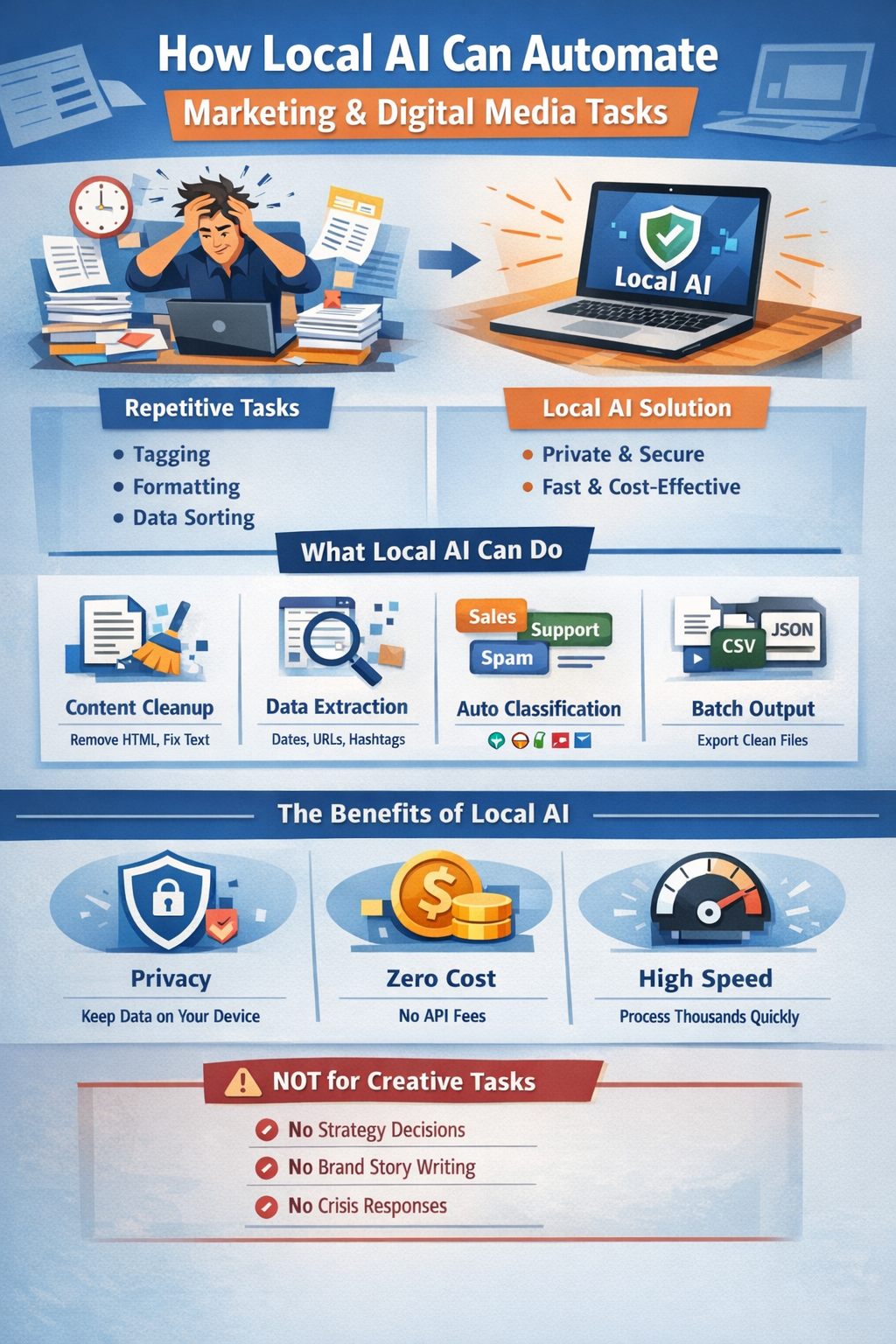
For digital marketers and social media managers, "creativity" is often only 20% of the job. The other 80% is logistics: reformatting content for five different platforms, tagging thousands of rows in a spreadsheet, standardizing ad copy, or pulling campaign IDs from endless reports.
These tasks are not creative. They are mechanical, repetitive, and volume-heavy. Yet, they consume hours of valuable time that could be spent on strategy or messaging.
This guide explains how local AI—running privately on your own device—can automate these static, high-volume marketing tasks. We will look at exactly what local AI can do, how it differs from cloud tools, and importantly, where it should not be used.
The Problem: Mechanical Volume in a Creative Field
Marketing operations often hit a bottleneck not because of a lack of ideas, but because of the sheer volume of execution required.
Consider a scenario where a team manages campaigns across three regions and four platforms. They might have:
- 500 variations of ad copy that need specific formatting.
- Monthly performance logs containing 10,000 raw lines of text that need to be categorized.
- A backlog of user-generated content that needs to be sorted by language or topic before a human reviews it.
Doing this manually is slow and error-prone. One missed tracking code or typo in a CSV file can derail reporting. Cloud-based AI tools are an option, but uploading sensitive internal data or customer logs to a public chatbot often violates privacy policies or incurs significant per-token costs.
Why These Tasks Are Static
The tasks described above share a common trait: they are deterministic.
- Rule-Based: If specific keywords exist, they belong to Category A. If not, Category B.
- Predictable Input/Output: A date format of MM/DD/YYYY always needs to become YYYY-MM-DD.
- No "Taste" Required: You do not need an opinion on the brand voice to extract a campaign ID or format a table.
Because these tasks follow rigid logic, they do not require human intuition. They require processing power and consistency—areas where local AI excels.
Why Local AI Is a Good Fit
Local AI refers to running models (like Llama 3 or Mistral) directly on your laptop or a dedicated on-premise server, rather than sending data to the cloud. For marketing operations, this offers three distinct advantages:
1. Privacy & Compliance: Customer lists, campaign performance data, and internal strategy docs never leave your machine. This is critical for agencies handling NDA-bound client data.
2. Zero Marginal Cost: High-volume tasks are expensive with paid APIs. If you need to categorize 50,000 comments, running a local model costs nothing but electricity.
3. Speed: There is no network latency. You can process thousands of text snippets in a batch loop as fast as your hardware allows.
What Local AI Actually Does
Local AI operates best as a high-speed, text-processing engine. Within the scope of marketing, allowed actions include:
- Content Handling: Cleaning up whitespace, removing HTML tags from scraped content, or standardizing capitalization across thousands of post drafts.
- Field Extraction: Scanning reports to pull out specific entities like Dates, URLs, UTM parameters, or Hashtags.
- Classification & Sorting: Labeling incoming messages as "Support," "Sales," or "Spam" based on keywords, or grouping ad copy by target region.
- Summarization (Non-Creative): Condensing rows of data into a summary table or extracting key metrics (Impressions, CTR) from unstructured text logs.
- Bulk Output: Converting unstructured notes into valid JSON or CSV files for upload to marketing platforms.
Local AI assists the process but does not replace professional marketing judgment or creative decisions.
Workflow: Automating Ad Copy Normalization
Here is a realistic, step-by-step workflow for using local AI to standardize a large batch of ad copy.
1. Export Data: Download your raw ad copy or social posts (e.g., 500 rows) into a CSV or text file.
2. Define the Rules: Create a strict system prompt.
Example: "You are a formatting assistant. For every input text: Remove emojis, ensure the first letter is capitalized, and append the campaign ID [CAMPAIGN-01] to the end. Do not change the wording."
3. Batch Process: Script a loop that feeds each row of text to the local model (e.g., using a tool like llama.cpp or a local server wrapper).
4. Field Extraction: Simultaneously ask the model to extract any mentioned product names into a separate 'Tags' column.
5. Output Generation: The model outputs the cleaned text and tags in a structured JSON format.
6. Review: A human marketer casually scans the output to ensure no context was lost (spot-checking 10-20 entries).
7. Final Upload: Import the cleaned, standardized data into your ad manager or social scheduling tool.
Realistic Example: Processing Campaign Logs
A mid-sized agency effectively used a local 7-billion parameter model to process raw feedback logs from a recent product launch.
- Input: 4,500 unstructured customer comments exported from social channels.
- Task: Classify sentiment (Positive/Negative/Neutral) and extract feature requests.
- Result: The local AI processed the file in under 20 minutes. It correctly tagged 92% of the comments, allowing the team to immediately identify a bug affecting login users.
- Cost: $0 (ran on an existing M2 MacBook Pro).
Limits: When NOT to Use Local AI
It is vital to understand the boundary. Local AI is a processor, not a strategist. Do NOT use it for:
- Creative Writing: It cannot write a "witty" or "heartfelt" brand story that resonates with a human audience.
- Strategy: It cannot decide which demographic to target or what your unique selling proposition should be.
- Crisis Communication: Never trust AI to draft responses to sensitive PR issues or angry customers without heavy human editing.
- Nuanced Tone: It struggles to detect sarcasm or subtle cultural references in high-stakes messaging.
Key Takeaways
- Automate the Boring Stuff: Use local AI for formatting, cleaning, sorting, and extracting data from high-volume text.
- Keep Data Private: Local models ensure sensitive campaign metrics and customer info stay on your device.
- Volume = Value: The more repetitive tasks you have (thousands of rows vs. ten), the more value local AI provides.
- Human Strategy First: Use the time saved on mechanics to focus on creative strategy, brand voice, and genuine connection.
Next Steps
Start small. Identify one "annoying" spreadsheet task in your marketing operations:
- Are you manually formatting ad copy for multiple platforms?
- Do you have thousands of social comments that need sentiment analysis?
- Are you extracting UTM parameters or campaign IDs from messy reports?
- Do you need to standardize capitalization or remove emojis from bulk content?
These are ideal candidates for local AI automation. Run a test using a local LLM on a small batch (50-100 items) to see how a mechanical assistant can clear your backlog, leaving you free to do the actual marketing.
For detailed implementation guides and model recommendations for marketing tasks, explore our technical documentation on local AI deployment in marketing environments.