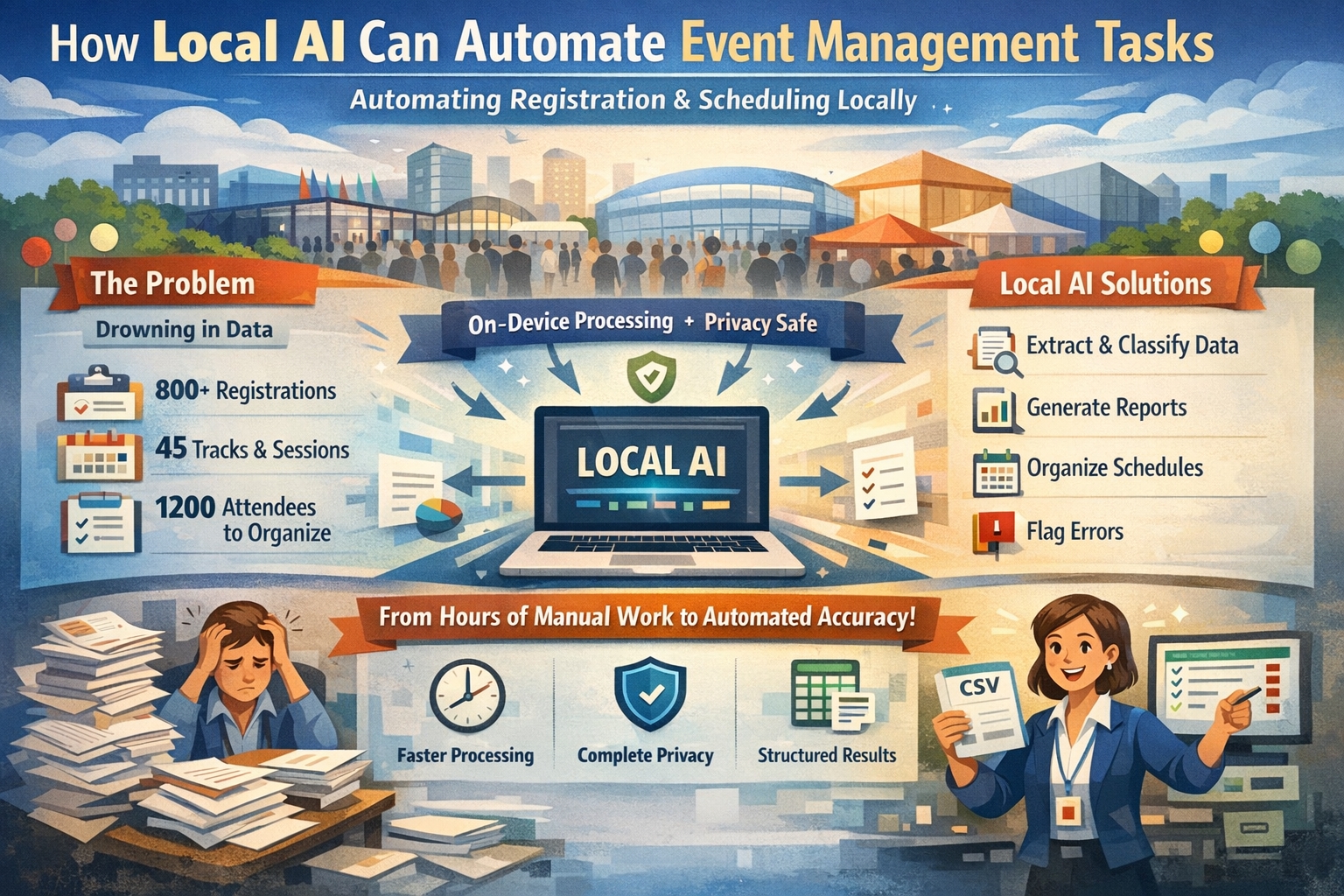
The Problem: Drowning in Registration Data and Schedule Management
Event operations teams face a recurring challenge: processing hundreds of registration forms after a conference opens, extracting attendee information from multiple ticket platforms, or organizing session schedules across dozens of tracks and venues. An event coordinator might spend 20 hours manually consolidating 800 registrations from three different sources into a single master list. A conference planner preparing for a multi-day event must categorize 1,200 attendees by ticket type, dietary restrictions, and session preferences to generate accurate headcounts for catering and room assignments.
These tasks are time-consuming, error-prone, and repetitive. Yet they're also predictable and rule-based—exactly the kind of work where local AI can provide meaningful assistance.
Why These Tasks Are Static
Registration processing, attendee classification, and schedule summarization follow consistent patterns. When you're extracting attendee names from registration forms, you're looking for specific fields: name, email, company, ticket type, and registration ID. When categorizing participants, you're matching them against predefined groups: VIP, general admission, speaker, sponsor, or press.
These tasks don't require judgment about whether an attendee should receive special treatment or creative decisions about event programming. They require consistent application of rules: extract contact information, sort by ticket type, flag incomplete registrations, generate attendance reports. The logic is repeatable across hundreds or thousands of records.
This deterministic nature makes them ideal candidates for automation—but only when the automation tool respects the sensitive, personal nature of attendee data.
Why Local AI Is a Good Fit
Event management involves personally identifiable information: names, email addresses, phone numbers, dietary restrictions, and accessibility needs. Sending attendee data to cloud-based AI services raises legitimate privacy concerns and may violate data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
Local AI runs entirely on your device. Attendee data never leaves your network. There's no API call to external servers, no data retention by third parties, and no risk of inadvertent disclosure. For event teams handling sensitive participant information, this privacy guarantee is essential.
Local AI also handles volume efficiently. Processing 2,000 registrations or 500 session schedules doesn't incur per-token cloud costs. The model runs locally, making it economical for high-volume, data-heavy workflows where cloud AI pricing would be prohibitive.
Finally, local AI produces deterministic outputs. Given the same registration data and the same classification rules, it returns consistent results—critical for event operations where accuracy and reliability matter.
What Local AI Actually Does
Local AI performs mechanical, rule-based actions on event data:
- Registration reading: Processes attendee lists, RSVP forms, ticket sales exports, and registration confirmations in CSV, Excel, PDF, or scanned formats
- Field extraction: Pulls attendee names, contact information, registration IDs, ticket types, company names, and session preferences
- Format normalization: Standardizes date formats, phone numbers, email addresses, and company names across multiple data sources
- Classification: Sorts attendees by ticket type, session track, dietary restrictions, or VIP status using predefined categories
- Summarization: Generates extractive summaries listing key metrics such as total registrations, attendees per session, cancellations, and no-shows
- Schedule organization: Extracts session times, speaker names, room assignments, and track information from event schedules
- Structured output: Exports findings to CSV, JSON, or spreadsheets for event management software, CRM systems, or badge printing
Local AI assists the process but does not replace professional judgment or operational decisions.
Step-by-Step Workflow: Registration Processing and Attendee Classification
Here's how an event operations team might use local AI to process and organize 1,500 conference registrations:
- Prepare registration data: Export registration lists from all ticket platforms (Eventbrite, custom forms, corporate registrations) into a single folder. Convert any PDF confirmations to text using OCR if needed.
- Define extraction rules: Specify which fields to extract: full name, email, company, job title, ticket type, dietary restrictions, session preferences, and registration date.
- Run batch processing: Use a local AI model (like Llama 3 or Mistral) with a prompt template that instructs the model to extract specified fields from each registration record. Process records in batches of 200.
- Normalize and classify: The model standardizes formats (e.g., converting all dates to YYYY-MM-DD) and classifies attendees into predefined categories: VIP, speaker, sponsor, general admission, student, or press.
- Flag incomplete records: Configure the system to flag registrations where required fields are missing (e.g., no email address, no ticket type) or data appears inconsistent (e.g., duplicate registration IDs).
- Generate reports: Export structured data showing total attendees by ticket type, dietary restriction counts for catering, session attendance projections, and VIP lists for special handling.
- Human validation: Event coordinators review flagged records and validate critical information before finalizing badge printing, room assignments, and catering orders.
Realistic Example
A corporate events agency managing a three-day industry conference needed to process 1,800 registrations from four different sources: online ticket sales, corporate group bookings, speaker registrations, and sponsor passes. Manually consolidating and categorizing this data would require approximately 30 hours of coordinator time at $50/hour ($1,500).
Using a local AI model running on a standard workstation, the team:
- Processed all 1,800 registrations in 4 hours of machine time
- Extracted and normalized attendee information into a single master spreadsheet
- Classified attendees by ticket type and generated session attendance projections for 45 breakout sessions
- Flagged 67 incomplete registrations for manual follow-up
- Reduced coordinator review time to 8 hours (validating outputs and resolving flagged records)
Total time saved: 22 hours. Cost savings: approximately $1,100. The team maintained complete data privacy and produced auditable, consistent results for badge printing and venue logistics.
Limits and When NOT to Use Local AI
Local AI is not appropriate for tasks requiring judgment, creativity, or interpersonal decision-making:
- Personalized recommendations: Do not use local AI to suggest which sessions an attendee should attend or create customized agendas based on interests
- Complaint handling: Guest complaints, last-minute changes, or special accommodation requests require human empathy and operational judgment
- Event programming: Designing session content, selecting speakers, or creating event themes demands creative planning and strategic thinking
- Conflict resolution: Handling double-bookings, venue changes, or attendee disputes requires professional event management expertise
- High-stakes decisions: Determining whether to cancel sessions, adjust schedules, or accommodate VIP requests should not rely solely on automated processing
Local AI is a tool for mechanical data processing. It accelerates repetitive work but cannot replace the judgment, creativity, and interpersonal skills that professional event managers provide.
Key Takeaways
- Local AI excels at static, high-volume event management tasks: registration processing, field extraction, classification, and summarization
- Privacy and cost advantages make local AI practical for event teams handling sensitive attendee data and large-scale operations
- Local AI reduces time and errors in repetitive tasks while preserving complete data confidentiality
- It is not a replacement for human judgment, creative planning, or interpersonal event management
- Best results come from combining local AI automation with professional event operations validation
Next Steps
If your event team handles high volumes of registrations, schedules, or attendee data, consider starting with a small pilot project:
- Identify one repetitive, rule-based task (e.g., extracting contact information from 100 registration forms)
- Set up a local AI model on a secure workstation
- Process a test batch and validate results manually
- Measure time savings and accuracy before scaling to larger events
For detailed setup guides and model recommendations for event data processing, explore our documentation and model selection guide.