Customer Support Operations: Automating the Mundane with Local AI
💡 Important: Consumer-Grade Hardware Focus
This guide focuses on consumer-grade GPUs and AI setups suitable for individuals and small teams. However, larger organizations with substantial budgets can deploy multi-GPU, TPU, or NPU clusters to run significantly more powerful local AI models that approach or match Claude AI-level intelligence. With enterprise-grade hardware infrastructure, local AI can deliver state-of-the-art performance while maintaining complete data privacy and control.
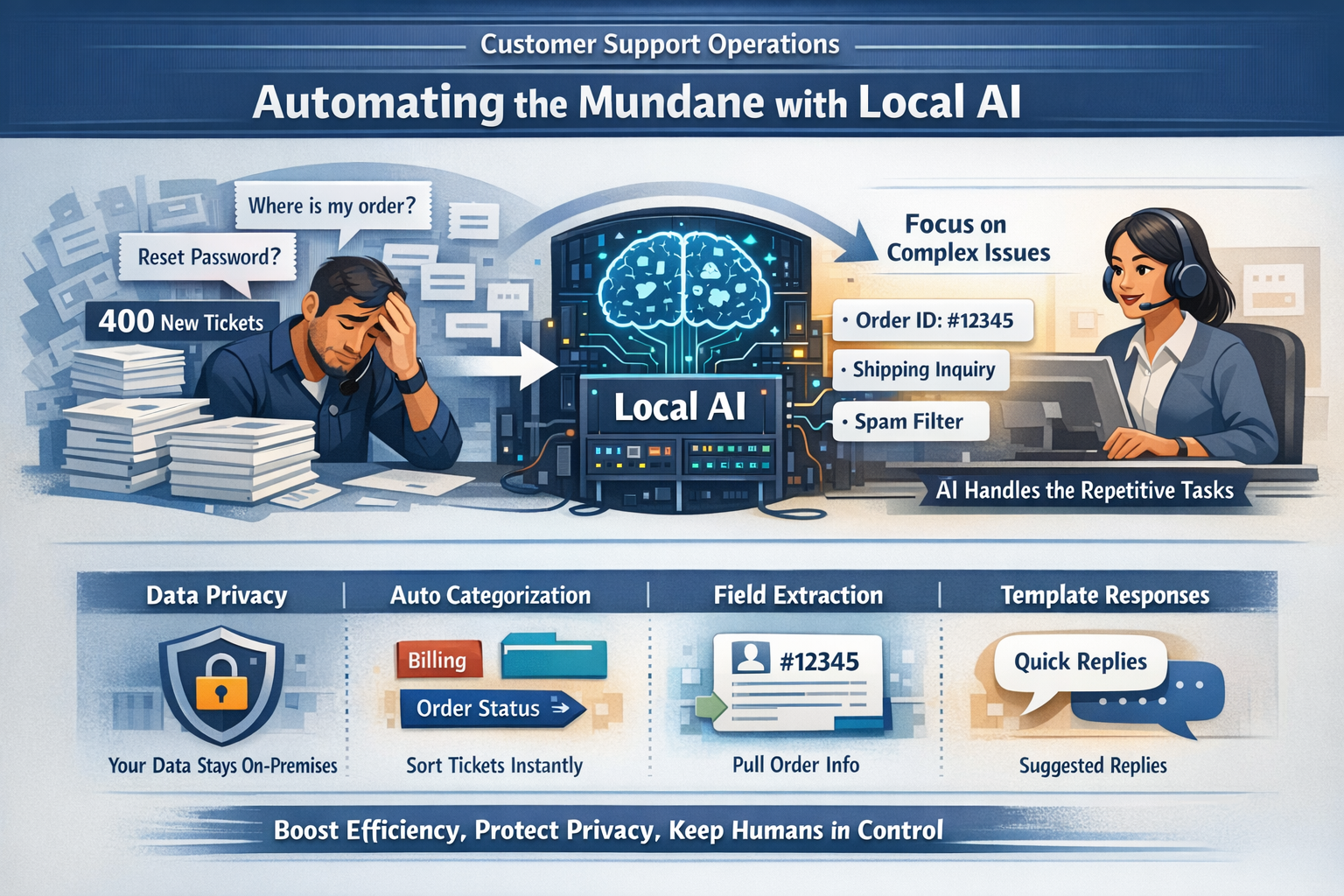
For customer support teams, the sheer volume of incoming requests can be overwhelming. Managers and agents alike know the fatigue of answering the same question for the fiftieth time in a day, or manually tagging hundreds of tickets just to get a sense of what's happening.
This article explains how local AI—artificial intelligence running on your own hardware, not in the cloud—can help support teams automate these static, high-volume tasks. We will look at exactly what local AI can do, how it protects customer privacy, and why it is a tool for efficiency, not a replacement for your human agents.
The Problem: The Burden of Repetitive Volume
The core challenge in many support operations isn't the difficulty of the questions, but the volume.
Imagine a Monday morning at a mid-sized e-commerce helpdesk. There are 400 new tickets.
- 150 of them are "Where is my order?"
- 50 are "I need to reset my password."
- 100 are spam or auto-replies.
- The remaining 100 are genuine, complex issues requiring human empathy and problem-solving.
Currently, human agents often have to open, read, and manually categorize every single one of those 400 tickets before they can even get to the 100 that actually need their skills. This "triage fatigue" leads to burnout, slower response times for critical issues, and increased error rates.
Why These Tasks Are Static
The tasks mentioned above—classifying a ticket as "Order Status" vs. "Returns," or extracting an Order ID from a subject line—are static.
They are predictable and deterministic.
- Rule-based: If the email contains "track my package," it is an "Shipping Inquiry."
- Repeatable: The logic doesn't change from customer to customer.
- No Judgment Required: Determining if a ticket is about a password reset does not require empathy, negotiation, or creative thinking.
Because these tasks rely on pattern recognition rather than reasoning, they are perfect candidates for automation.
Why Local AI Is a Good Fit for Support
While cloud-based AI tools exist, local AI (using on-device models like Llama 3 or Mistral via GGUF) offers distinct advantages for customer support operations:
1. Data Privacy & Compliance: Support tickets often contain Personally Identifiable Information (PII)—names, addresses, phone numbers. Local AI allows you to process this data entirely within your secure network. No customer data is ever sent to a third-party API.
2. Cost Efficiency: Cloud AI often charges per "token" (word part). Processing thousands of tickets a day for categorization can get expensive quickly. Local AI runs on your existing hardware (or dedicated local servers) for a fixed electricity cost, regardless of volume.
3. Low Latency & Reliability: Local models don't depend on internet bandwidth or external API uptime. They can process chat logs or tickets as fast as your hardware allows, ensuring your internal dashboards are always up to date.
What Local AI Actually Does
Local AI is strictly a mechanical processor in this context. It does not "think" or "care" about the customer; it simply manipulates text based on patterns.
In a support workflow, allowed local AI actions include:
- Ticket / Chat Handling: Reading raw text from emails or chat logs and cleaning it (removing HTML tags, normalizing whitespace) for processing.
- Field Extraction: Automatically pulling out structured data like Order IDs, SKU numbers, dates, or email addresses from unstructured message bodies.
- Classification & Sorting: Tagging tickets by topic (e.g., "Billing," "Technical," "General"), urgency (e.g., "High," "Low"), or sentiment (e.g., "Frustrated," "Neutral") to route them to the right queue.
- Template-Based Responses: Suggesting a standard pre-written response snippet based on the classified intent (e.g., suggesting the "Refund Policy" snippet if the intent is "Refund Request").
- Summarization: Creating a bulleted summary of a long chat thread so an agent can quickly get up to speed before taking over.
Crucially: Local AI assists the process but does not replace professional customer support judgment or human decision-making.
Workflow: How to Implement Local AI in Support
Here is a practical, step-by-step workflow for integrating local AI into a support stack:
1. Ingestion: Your system fetches the latest batch of unassigned tickets from your helpdesk (e.g., via API export or CSV).
2. Sanitization: A script removes unnecessary headers and formats the text.
3. Classification Pass: A small, fast local model (like Phi-3-mini or similar) scans each ticket and assigns a category tag (e.g., Category: Shipping).
4. Extraction Pass: The model identifies and extracts specific entities, such as Order ID: #12345 or Customer_Email: user@example.com.
5. Routing: A simple script moves the ticket to the appropriate queue based on the tags. "Shipping" goes to the Logistics Team; "Technical" goes to Tier 2 Support.
6. Agent Assist: When an agent opens a ticket, they see a private note populated by the AI:
- Summary: "Customer asking for refund on order #12345 due to delay."
- Suggested Template: "Apology for Delay + Refund Process"
7. Human Action: The agent reviews the suggestion, edits it for tone and specific context, and sends the reply. The human remains the final authority.
Realistic Example: The "Monday Morning" Triage
Consider "TechGear Solutions," a mid-sized electronics retailer.
- Volume: They receive 1,000 tickets every weekend.
- Old Process: Three agents spent 4 hours each on Monday morning just reading subject lines and assigning tickets to queues. That's 12 man-hours lost to sorting.
- New Process with Local AI:
- A script runs at 8:00 AM on a local server with a GPU.
- It processes all 1,000 tickets in about 20 minutes.
- It successfully categorizes 900 of them with high confidence.
- It flags 100 as "Ambiguous" for human review.
- It extracts Order IDs for 850 tickets and pre-loads the customer's order status from the database into the ticket sidebar.
- Result: When agents log in at 9:00 AM, the "Returns" queue is already populated, and they can start solving problems immediately. The 12 hours of manual sorting are reduced to zero.
Limits: When NOT to Use Local AI
While powerful, local AI is not a universal fix. It inherently lacks understanding of context, nuance, and human emotion.
Do NOT use local AI for:
- Complex Troubleshooting: If a customer has a unique technical issue that isn't in the manual, the AI cannot "figure it out." It will hallucinate or provide generic, unhelpful advice.
- Escalations & Conflict: Determining if a customer is roughly "upset" is fine, but deciding how to de-escalate a furious client requires human empathy and negotiation skills.
- Personalized Advice: AI should not be recommending products or financial choices based on a customer's life story.
- Automated Sending: Never let the AI send emails directly to customers without human review. The risk of a nonsensical or insensitive reply is too high.
Key Takeaways
- Efficiency: Local AI excels at the crucial but boring "janitorial" work of support: sorting, tagging, and extracting data.
- Privacy First: Running models locally ensures that sensitive customer conversations and PII never leave your secure infrastructure.
- Human-in-the-Loop: The goal is to free up your human agents to handle the complex, high-value interactions that actually build customer loyalty, not to replace them.
By deploying local AI for these specific, static tasks, support teams can lower costs, reduce agent burnout, and improve response times—all while keeping data safe and control firmly in human hands.
Next Steps
Identify high-volume, repetitive tasks in your support operations:
- Are agents spending hours manually categorizing tickets?
- Do you need to extract order IDs or customer information from unstructured emails?
- Are you routing tickets based on keywords that could be automated?
- Do you want to provide agents with suggested responses to speed up reply times?
These are ideal candidates for local AI automation. Start with a pilot project processing 100-200 tickets to test accuracy and workflow integration before scaling to full production volumes.
For detailed implementation guides and model recommendations for customer support tasks, explore our technical documentation on local AI deployment in support environments.